Table of Contents
Product Marketing Managers (PMM) are crucial in bridging the gap between product and marketing. However, there often needs to be more clarity regarding the budget allocation for PMMs.
In an organization, Product marketing stands at a crossroads where products, markets, and finances converge, holding the reins of Brand positioning, market penetration, and customer engagement strategies.
Yet amidst the intricate role, one element often emerges as a formidable challenge: Budgeting.
This blog ventures into the heart of this challenge, drawing from diverse experiences and insights gathered from PMMs across geography.
It sheds light on the intricacies of budget resource distribution, prioritizing spending, and budget allocation to ensure that their product reaches the right market and thrives in it.
Do PMMs Have a Dedicated Budget?
The landscape of budget allocation for PMMs is of varied experiences and practices.
Drawing insights from over 30 Product Marketers, we’ll delve into budget allocation nuances, spending priorities, and strategies.
“If the head of PMM reports to the CEO directly, they would have a budget. Otherwise, it sits with the Head of Marketing. But of course, one can spend a % marketing budget on PMm core activities.”
Here are the learnings
- Varied Experience: Some PMMs report having a dedicated budget, while others rely on shared resources from departments like Product or Marketing.
- Dependence on Company Structure: Budget allocation to PMMs also depends heavily on the company’s internal structure and reporting hierarchy. Often reflecting how they perceive and value the role of product marketing in their corporate ecosystem.
Challenges and Strategies in PMM Budget Management
Managing the PMM budget is like balancing a thin rope between significant product launches on a tight budget.
The challenge is not just about managing the money; it’s also about proving why each expense is essential for the product’s success.
Product Marketers must be good with different teams and departments because they often have to pull resources and put them together in a way that makes the most sense to their marketing plan.
The key to doing well in this role is working with others effectively and being smart about using your budget.
How PMMs Spend Their Budgets?
The budgetary allocation by PMMs encompasses a spectrum of activities essential for the product’s life cycle.
From sponsoring insightful collaterals crafted by third-party analysts that may include performance benchmarks and competitive landscapes to sponsoring product-specific promotions at trade shows and user groups.
The budget also includes dedicated investment into customer interaction, content creation, and targeted product marketing campaigns, each tailored to the unique messaging and positioning of the product.
6 steps to create a Product Marketing budget
Step #1: Calculate the cost of Essential Components of Product Marketing
This category encompasses the critical elements necessary for effective product marketing.
It includes costs of obtaining external market insights from third-party analyst firms, direct promotional activities tailored to the product and engaging with customers through interviews.
These components are vital for understanding market trends, positioning the product effectively, and gaining customer feedback.
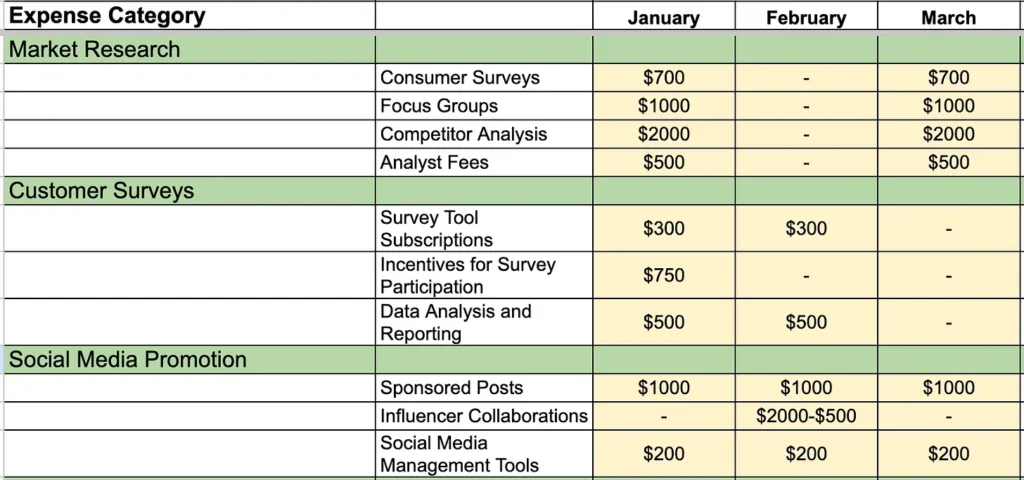
- Third-Party Analyst Firms: Expenses for external market research, analyst reports, competitive analyses, and industry insights.
- Product-Specific Promotion: Costs associated with promoting the product, such as advertising, user groups, trade shows, and third-party reviews.
- Customer Interviews and Advisory Boards: Expenses for conducting customer interviews and setting up customer advisory boards, including any related travel and hospitality costs.
Step #2: Estimate Basic Expense
The fundamental cost of creating and distributing marketing content falls under this category.
It includes budgeting for content creation across all formats, managing email marketing campaigns, including emailing tools for content creation, and conducting market research to understand consumer behavior and the competitive landscape.
These expenses are foundational to any marketing strategy, ensuring consistent communication and market understanding.
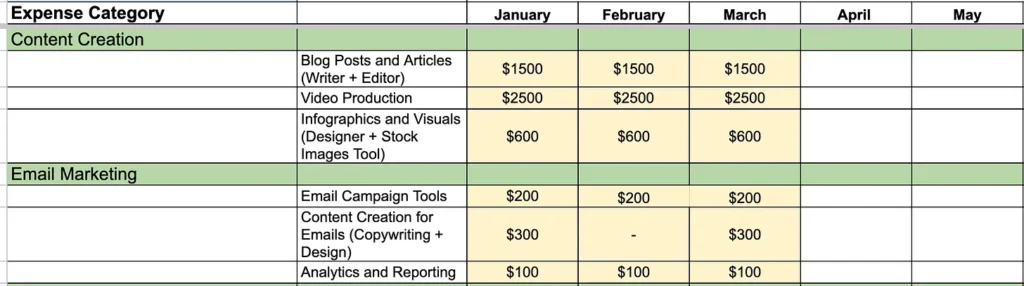
- Content Creation: This includes costs for creating blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, and other marketing collateral.
- Email Marketing: Budget for email campaign tools, content creation, and analytics.
- Market Research: Funds allocated for conducting consumer surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis.
Step #3: Calculate the Fixed Cost
This category covers the more predictable, non-variable costs associated with events, tradeshows, and partnerships.
It includes all expenses associated with participating in Trade shows, organizing promotional events, and costs arising from strategic partnerships and collaboration.
These fixed costs are crucial for planning and networking opportunities and amplifying product visibility in the market.
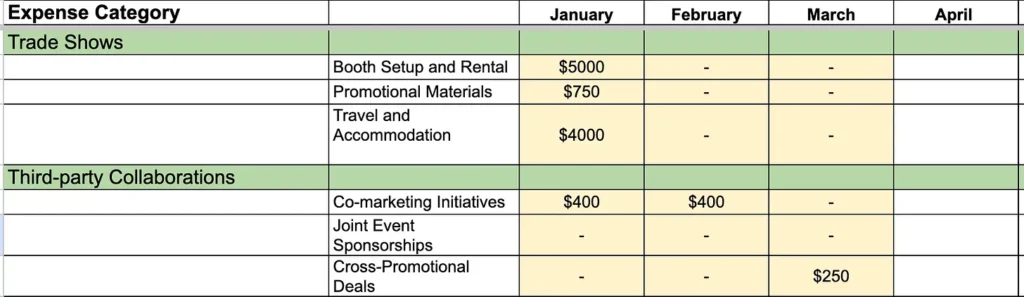
- Events and Trade Shows: Costs for booth setup, rental, promotional materials, and associated travel and accommodation for trade shows and other promotional events.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Budget for joint marketing initiatives, event sponsorships, and cross-promotional deals.
Step #4: Calculate the Technology Cost
Here, the focus is on the investment in marketing technology and tools.
This includes software for customer relationship management, data analytics platforms, and social media management tools.
Technology costs are essential for modern marketing operations, enabling efficient campaign management, data analysis, and customer engagement.
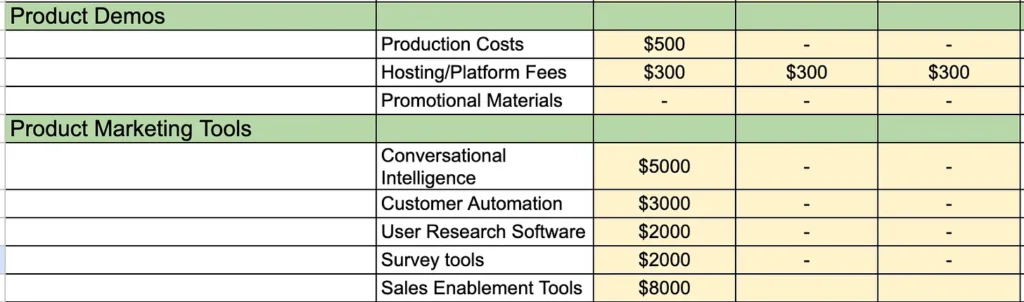
- Marketing Tools and Platforms: Investment in marketing software and tools, such as CRM systems, analytics platforms, social media management tools, and other technology solutions that support marketing efforts.
Step #5: Estimate your miscellaneous costs
This category is reserved for unforeseen expenses and innovative marketing experiments. It accounts for unexpected costs during marketing initiatives and provides a buffer for exploring new marketing tactics, tools, or campaigns.
Allocating funds for miscellaneous costs ensures flexibility and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions or to capitalize on new opportunities.
- Unexpected Expenses: Allocation for unforeseen costs that may arise during the execution of marketing plans.
- Innovation and Experimentation: A portion of the budget for trying new marketing tactics, tools, or campaigns that may fall outside the regular marketing activities.
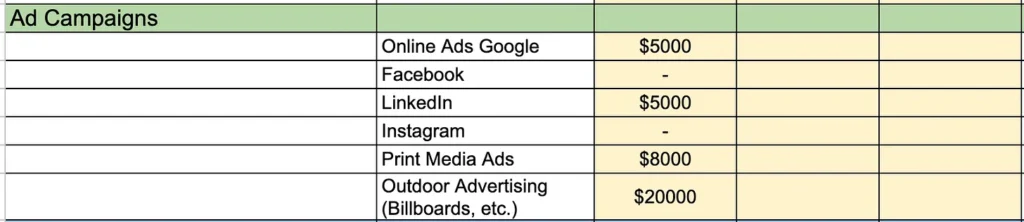
Step #6: *Estimate Ad Campaign Costs
“It depends on what you can get away with in your company. Often, you would be stopped because you are on some other marketing team’s turf. It’s risky to try a campaign without corporate buy-in.”
Product Marketing Managers (PMMs) are responsible for a product’s overall positioning, messaging, and go-to-market strategy.
This can include overseeing or collaborating on ad campaigns, primarily when these campaigns are directly related to product launches, feature updates, or specific product-focused promotions.
PMM might work closely with Ads or Demand Generation teams to ensure the Ads align with the strategy.
However, in many organizations, the creation and management of ad campaigns are primarily handled by a separate marketing or advertising team, like a Demand Generation team.
PMMs in these settings might provide input on the product-related aspects of the campaign but might not directly control the budget or execution of the campaigns.
In summary, whether ad campaigns fall under the purview of Product Marketing can vary based on how a company organizes its marketing functions and allocates responsibilities between different teams.
In some companies, PMMs have direct involvement and budget allocation for ad campaigns, while in others, they may play a more consultative role, focusing on product strategy and messaging.
Tips for managing Product Marketing budget
Here are some tips for managing your Product Marketing budget effectively throughout the year:
- Align with Business Goals: Ensure your budget aligns with the broader business objectives. Understand the company’s key performance indicators (KPIs) and tailor your budget to support these goals.
- Prioritize Wisely: Identify and prioritize high-impact initiatives that promise the greatest return on investment (ROI).
- Stay Agile: Be prepared to reallocate funds as needed to capitalize on new opportunities or adjust to shifting market dynamics.
- Leverage Cross-Functional Collaboration: Product marketing doesn’t operate in a silo. Work closely with sales, product development, and other departments to ensure your budgeting decisions support broader company initiatives.
- Track your spending: It is essential to track your spending to stay within your budget. This will also help you to identify areas where you can save money.
- Embrace Experimentation: Set aside a portion of your budget for testing new strategies and tools. This might include experimenting with new marketing platforms, trial campaigns, or emerging market trends.
- Use free and low-cost recruitment tools: Several free and low-cost tools are available. Try them out.
- Plan for Scalability: As your product and market presence grow, your budgeting needs will evolve. Plan for scalability by building a flexible budgeting framework accommodating growth and change.
- Spend on skill development: Learning and skills development of the team are just as important as tech skills in the industry.
- Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keep your finger on the pulse of the latest marketing trends and technologies. Staying informed helps you make more educated decisions about where to allocate your budget for maximum impact.
Plan your recruiting budget effortlessly.
Ensure that your cost does not increase exponentially for any given year and should be in sync with the business goal, revenue growth, and the number of customers. Download a sample budgeting sheet for 2024.



