Table of Contents
Data management is the strategic art of collecting, organizing, and utilizing data to fuel marketing initiatives. Think of it as the engine that powers effective campaigns, enabling businesses to make informed decisions, target the right audience, and optimize their marketing strategies.
Data management involves two key aspects: handling external data sources, which include information from various channels outside your organization, and nurturing internal data, such as user insights and customer data. The goal? To transform raw data into actionable insights, ensure your marketing efforts are reasonable and exceptional.
This blog will delve deeper into data management, uncovering its secrets, techniques, and practical applications.
Throughout my career, I’ve had the privilege of working with some fantastic organizations, and today, I’m here to share some of the data management strategies that have worked wonders for us.
Now, let’s roll up our sleeves and get into the nitty-gritty of the two types of data that most organizations hold:
External Data: This category comprises data from non-registered users, individuals who may not have accepted terms and policies, or data procured from third-party providers.
Internal Data: On the flip side, internal data encompasses information from users who have registered or shared their data on your platform through various forms.
Keeping external this data segregated in a dedicated sheet is crucial. Regular maintenance is vital here to ensure no spam or unsubscribed data lurks within this list.
Every time you email a customer, this data must undergo sanitization. The emails can target a broader audience or carry specific marketing content (TOFU/MOFU or BOFU).
The goal?
To identify any traces of spam, blocks, or unsubscribes and cleanse them from our records.
External Data Buckets
In the realm of external data, employ a systematic approach to categorize and manage valuable information into three distinct buckets:
- Green Verified 🟢 : This category includes data that has been meticulously collected and confirmed using a reliable third-party tool. It’s the cream of the crop, ensuring the highest level of accuracy.
- Yellow Verified🟡 : The yellow verified data consists of user information whose email IDs couldn’t be confirmed by third-party tools, often due to server-level blocks. To enhance its reliability, proactively engage with these users through email campaigns to verify their inbox delivery. Any data lingering in this bucket for over 30 days is promptly moved to the green verified category.
- Red Verified🔴 : Data in this category is either incorrect or non-existent, and promptly remove it from our database to maintain data integrity.
- Mapped Accounts: Identify these as top targets or wish list accounts. Collaborating closely with our sales team, create a dedicated green verified data pool containing key stakeholders. This pool is the foundation for our targeted campaigns, allowing us to penetrate these accounts effectively.
Additionally, there are instances where you acquire bulk data from third-party sources, and its verification status may need to be discovered.
In such cases, swiftly initiate email verification processes to confirm their green status and allocate them to the appropriate bucket.
This structured approach ensures that our external data remains accurate, reliable, and aligned with our marketing objectives.
Cleaning & Targeting External Data
When it comes to maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of our external data, a systematic approach is vital:
- Immediate Removal: If a user from the external database signs up on our website after receiving any communication, remove them from the external data list. This ensures that you don’t inadvertently target engaged users through our communication.
- Filtering Unwanted Data: Remove any data that has been blocked, unsubscribed, or marked as spam from the external data sheet. This ensures that focused communication efforts are made.
- Upgrading Yellow to Green: Once an email is successfully delivered, Yellow verified data, representing users whose emails couldn’t be initially confirmed, should be transitioned to green verified status. Remove all blocked, marked as ‘spam,’ ‘unsubscribed,’ or ‘found to be incorrect’ from the Yellow Verified category.
- Comprehensive Data Mapping: For green verified data, it’s essential to map the users with their respective company names, designations, city locations, and company verticals. Employ manual methods to acquire this information if company data needs to be included. Once you have comprehensive user details, they should be treated as mapped accounts, as in Point №6.
- Verification for Mapped Accounts: Initiate email confirmation processes for mapped accounts to determine their green verified status. Retain correct email addresses while rectifying the incorrect ones through permutations-combinations logic or third-party tools. It’s also advisable to identify both official and personal email IDs.
This opens up opportunities for running targeted ads using platforms like Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn, focusing on reaching the right audience through email campaigns and banner ads. - Tailored Content and Campaigns: Categorize all mapped accounts by similar designations and verticals. This segmentation allows for delivering highly relevant content, such as case studies, to specific groups. For instance, content related to Chief Technology Officers (CTOs) can be directed to all CTOs, while HR-related content can be sent to senior HR professionals. Paid campaigns and drip marketing are practical tools for ensuring that content aligns with the recipients’ interests and roles.
This comprehensive approach maintains the quality of our external data and maximizes the impact of our marketing efforts by delivering tailored content to the right audience segments.
Always maintain a real-time check on all kinds of external data status. Create a summary sheet with a ‘status’ tab in a table suggesting how many yellow/green verified data for every product is available.
Creating a Mapped Account List
Now, let’s dive into the nuts and bolts of creating a mapped account list. This list is no ordinary roster; it’s a compilation of companies and accounts our sales team identified as having substantial business potential.
Some accounts may fall under the enterprise category, while others could belong to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs).
When assembling this crucial list, several vital pieces of information need to be gathered for each account:
- Business Verticals: This refers to the industry type in which each account operates. Whether it’s banking, manufacturing, or any other sector, understanding their business vertical is essential for tailoring our marketing efforts effectively.
- Designation of Key Stakeholders: Knowing the key decision-makers within these accounts is paramount. Identifying their roles and responsibilities allows us to target the right individuals with our campaigns.
- Names & Email IDs: Collect these key stakeholders’ personal and professional email IDs. This enables us to establish direct lines of communication with them, enhancing our engagement.
- City and Country: Knowing the location of these accounts, down to the city and country level, helps us personalize our outreach and align our strategies with regional considerations.
Categorize these accounts based on their business verticals to further enhance our understanding.
For example, an organization might fall under the “Manufacturing” vertical, with a sub-vertical specifying their particular niche, such as “Electronics Manufacturing.”
Here’s a list of some common business verticals to give you an idea:
- AGRICULTURE AND ALLIED INDUSTRIES
- AUTOMOBILES
- AUTO COMPONENTS
- AVIATION
- BANKING
- CEMENT
- CONSUMER DURABLES
- EDUCATION AND TRAINING
- ENGINEERING AND CAPITAL GOODS
- FINANCIAL SERVICES
- GEMS AND JEWELLERY
- HEALTHCARE
- INFRASTRUCTURE
- INSURANCE
- IT
- ITES
- MANUFACTURING
- MEDIA AND ENTERTAINMENT
- OIL AND GAS
- PHARMACEUTICALS
- PORTS
- REAL ESTATE
- RETAIL
- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
- SERVICES
- STEEL
- TELECOMMUNICATIONS
- TEXTILES
- TOURISM AND HOSPITALITY
By meticulously organizing our mapped account list and gathering these essential details, you’re setting the stage for highly targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
Internal Data
Now, let’s delve into the intricacies of internal data, a treasure trove that can be categorized into three distinct types:
TOFU (Top-Of-The-Funnel):
- Capturing the Introduction: TOFU data represents users who have just entered our business category or engaged with introductory content. They may have perused our preparatory materials, subscribed to our content, or filled out a form to access it. For instance, a user who lands on our blog article titled “Job-hopping makes Millennials better hires” subscribes to our blog after reading it falls into this category. Similarly, anyone who visits a webinar page and completes the form for access belongs here.
Typical Users: TOFU data typically comprises blog subscribers, webinar attendees, ebook downloaders, and those who engage in roundtable discussions.
MOFU (Middle-Of-The-Funnel):
- Beyond Beginners: MOFU data encompasses users with a better-than-beginner understanding of our business category. They have transitioned from TOFU to MOFU by engaging with content that delves deeper into our products or services. A prime example of MOFU content includes ebooks.
Typical Users: This category comprises ebook downloaders, consumers of whitepapers, and anyone who engages with content that takes them a step further into our product or business offerings.
BOFU (Bottom-Of-The-Funnel):
- Expressing Genuine Interest: BOFU data houses users who have shown a keen interest in our products or services. They often make a tangible commitment by signing up for trials or demos. These users are at the stage where they are considering or actively evaluating our offerings.
Typical Users: BOFU data encompasses individuals who have signed up for website trials, requested product demos, participated in roundtable discussions, expressed interest in product trials or demos post-webinar, engaged in chat interactions, or reached out via direct mail using organization contact email IDs while showing a product interest.
By categorizing internal data into these three distinct buckets, one can gain valuable insights into user intent and tailor our marketing strategies accordingly.
Nurturing TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU Data
Once the data has been categorized into TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU, it helps build momentum and effectively nurture these leads. Here’s how to do it:
- Drip Campaigns: Create a well-structured drip campaign within your CRM or email marketing platform. This campaign is a dynamic tool to continually engage and move our TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU data up the conversion ladder. Maintaining a growing and active base for each data category is crucial to customizing your products or services.
- Remarketing Ads: Extend your reach by running remarketing ads on platforms like Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn. By mapping these ads to their current organizations, you can maintain brand visibility and reinforce your message to these leads.
- BOFU Engagement: For BOFU data, it’s all about expediting the conversion process. This involves encouraging them to take the first step, such as scheduling a usage demonstration or demo call. As the trial period draws closer to expiry, the drip campaign should create a sense of urgency to encourage purchase.
- Post-Trial Follow-up: If a customer doesn’t convert after the trial period, initiate contact to understand their reasons and gather feedback. Create a separate list for non-converted trials, often called “Dormant Prospects.” Send a series of three emails at intervals of five days, three months after the trial period expires — to reopen the discussion.
- Complex Product Support: It’s crucial to ensure that customers thoroughly understand complex products. Offer product walkthroughs and a seamless onboarding experience to facilitate their engagement. Keep an eye on their actions within the platform and gently encourage them to take the desired steps.
- Feedback Loop: After one month of non-conversion, reach out to these leads again, seeking their feedback. This feedback can provide valuable insights into any barriers preventing conversion.
Implementing these nurturing strategies helps maintain engagement with our leads and increases the chances of conversion.
Remember, the key is to keep the lines of communication open and adapt your approach based on their behavior and responses.
Customer Data
In the dynamic landscape of customer data, one can categorize it into two distinct types: existing customers and churned customers.
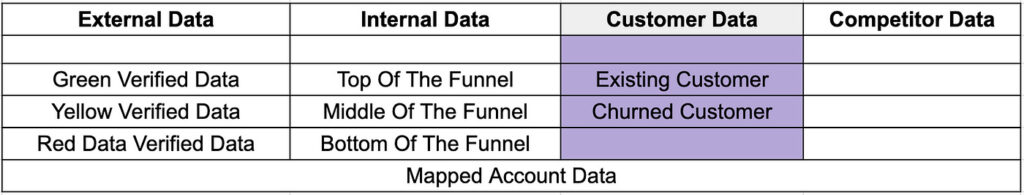
Existing Customers:
It’s all about fostering growth and expanding our relationship with our existing customers. Here’s the game plan:
- Profile Enrichment: Dive deep into our existing customer accounts and identify opportunities for cross-selling. For instance, if a customer has already purchased one of our products, there’s a ripe opportunity to introduce them to another business unit (BU) within their organization that could benefit from the same product. Additionally, one can pitch complementary products to the same account, enhancing their overall experience.
- Strategic Timing: When pitching to another BU within the same company, timing is crucial. Wait until after a managed service campaign concludes. However, if it’s not a managed service campaign, initiate outreach as early as the second month following the sale. Our pitch should emphasize the value and benefits of the additional product or service, illustrating how it can further address their needs and objectives.
Churned Customers:
For customers who have churned, it’s imperative to handle them with care and a clear plan in mind:
- Separate Bucket: All churned companies should be isolated into a different category. You can activate engagement with these customers after a six-month hiatus.
- Managed Service Campaigns: Recognize that churn is nearly inevitable for managed service campaigns, often reaching 100%. To address this, one must have a well-defined strategy to re-engage with these customers.
- SaaS Product Approach: For SaaS products, the first email to churned customers should promptly inform them that their account has been deleted. This initial contact should also seek their valuable feedback on their experience.
- Strategic Re-Engagement: Following the removal of their account, wait for three months before reaching out again. This time, three emails should be crafted to secure another appointment to discuss our latest products and how they align with the customer’s requirements.
By effectively managing our existing and churned customer data, you not only nurture current relationships but also have the potential to rekindle ones that have momentarily lapsed.
Competitor Data
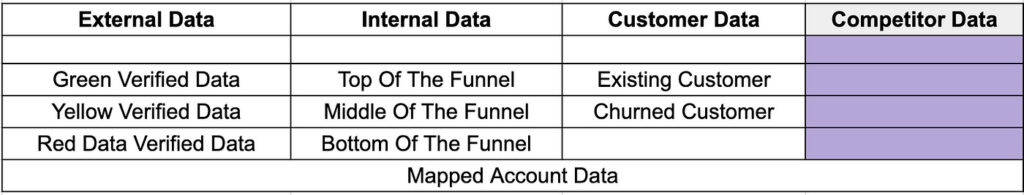
In the ever-evolving landscape of marketing, it’s essential to keep a watchful eye on your competition. One valuable source of data that often goes overlooked is competitor customer data. Here’s why you should consider harnessing this helpful resource:
Turning the Tide: When you’re aware that the need for your product or service is already established within your industry, it presents a unique opportunity. Competitor customer data can be a goldmine waiting to be explored. These individuals or companies have demonstrated a genuine interest in a product or service similar to yours.
Sources of Competitor Customer Data: You can acquire competitor customer data from various sources, including competitor user logos, case studies, platforms like G2 Crowd, Trust Pilot, and more. These sources can provide insights into potential leads actively engaged with your competitors.
Converting Competitor Customers: The art of converting competitor customers is fascinating. A quick search on Google will reveal an array of hacks and techniques for effectively wooing competitor customers. (Or another blog on this!)
Managing B2B Email Campaigns
Actively classify our B2B mailers into three distinct buckets: TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU. These buckets remain dynamic, allowing us to adapt and refine our strategies based on specific objectives and performance metrics.
Bucket Benchmarks: Each bucket has its own benchmarks that guide our efforts. These benchmarks act as our North Star. Our primary goal remains actively generating more trials and, eventually, conversions from these prospects.
Actively leverage various email marketing tools to execute our drip campaigns seamlessly. Our Data Intelligence team actively sets up these mailers and ensures their active integration with our ecosystem, including platforms like WordPress, CRM systems, websites, and other third-party tools.
The Data Intelligence actively monitors the performance of our drip campaigns weekly. This actively involves tracking key metrics and actively extracting actionable insights. These insights are then actively shared with the broader team, ensuring all strategies align with our overarching goals.
Data Intelligence Team Responsibilities
- Mastering CRM Operations: It’s crucial for the team to actively familiarize themselves with every aspect of the CRM, from its processes to its management.
- Data Input Management: They actively ensure that all trial and demo data is promptly entered into the CRM. Some data sources, like chat interactions, webinars, roundtable discussions, and inbound emails, require manual data input.
- Dormant Account Identification: After every 45 days of trials and demos without conversion, the team actively flags these accounts as inactive accounts, enabling the data team to prioritize their efforts more effectively.
- Conversion Tracking: The team actively tracks monthly conversions on CRM for domestic and international segments, providing us with critical insights into our performance.
- Integration with Marketing Tools: The team actively integrates the CRM with various marketing tools such as Mailchimp, Drip campaigns, and other third-party solutions to streamline our marketing efforts.
- Complete Conversion Reporting: Accurately report all conversations on CRM. This encompasses domestic and international conversions, focusing on meticulous capture, even for manual invoicing.
- Stakeholder Involvement: The data intelligence team actively involves and empowers all marketing stakeholders to refer to the CRM for lead, conversion, and churn tracking. This collaboration ensures that everyone remains aligned with our objectives.
- Training Initiatives: The team actively trains new and existing employees on the CRM system, ensuring that all team members are well-equipped to utilize its functionalities effectively.
By meticulously categorizing, cleansing, and harnessing the power of data, businesses can make informed decisions, engage with their target audience more effectively, and ultimately drive growth.
Remember, data management is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process that requires dedication, adaptability, and a commitment to delivering exceptional value to your audience.



